Customer interactions today are more data-driven than ever, but when it comes to AI’s role in improving customer service, results are mixed. Will the advances in generative AI drive a return on the enterprise AI investment? After all, we have heard before the grand proclamations about how robots are likely to replace humans everywhere. Once the dust settles, will generative AI simply give us fancier chatbots, or will it actually change the way companies design and implement customer service?
Will AI Change Customer Service?
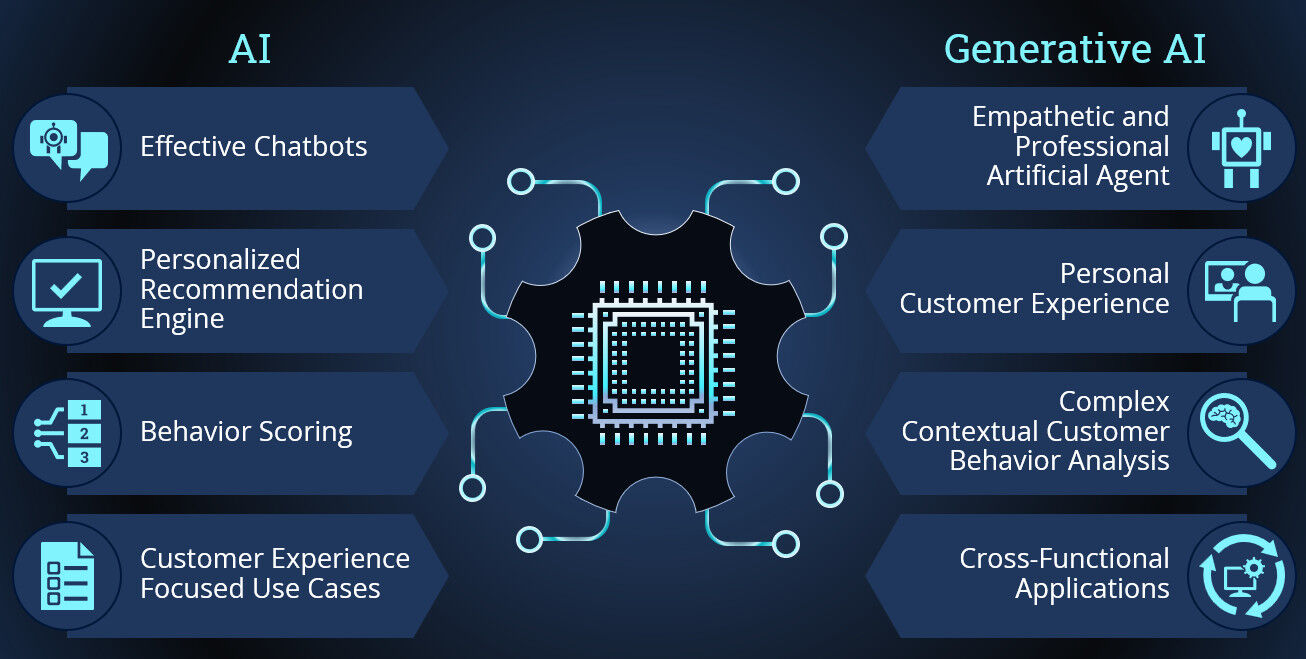
Three markers of superior customer service are professionalism, empathy and effectiveness. Until now, customer service solutions have focused on effectiveness by enabling faster response to customer needs. Generative AI can go further. Today’s AI is mostly tackling frequent reoccurring and simple customer service issues, while complex problems are routed to humans. But generative AI has the potential to allow AI agents to address more complex and unforeseen customer needs. While AI can perform sentiment analysis, generative AI can create custom messaging with the appropriate tone and adjust for different situations and types of customers. An AI-powered virtual assistant would be both highly effective, professional and able to learn to express empathy personalized to each user.
Another major shift is the impact on data itself. Generative AI can significantly enrich data collection by enabling the creation of new synthetic data. The potential to fine-tune recommendation engines and offer more personalized and accurate interventions can drive real benefits to the customer experience.
AI Use Cases Across Industries
AI is already making waves in enterprises. The following are examples across several industries.
- AI in Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals Industries
Consider claims management in healthcare or pharmaceutical prescription filling services. Typically, these kinds of customer service interactions are recorded and require a dynamic response from agents. They both also require large data collection efforts, bringing together data from disparate sources into a single system. Generative AI contextual intelligence capabilities combined with vectorized databases of proprietary enterprise content enable comprehensive analysis of relationships within large unstructured datasets, allowing a claim to be initiated and partially processed without a human trigger. Once a model concludes that the claim would not be rejected due to the nature of the claim or potential fraud, generative AI can then take the next step and contact the customer in the most effective and appropriate manner.
- AI in the Travel Industry
In the travel industry, upselling customers is a key revenue generator that requires the agent to adapt based on the flow of their interaction. Many agents are uncomfortable with upselling, creating mixed results. Automation of processes like check in and check out also obscures the opportunity to present an upsell. Unlike a human agent, generative AI can access pertinent information about availability, and instead of simply listing every available upgrade option, can learn from historic upsell behavior and generate a custom proposal that is most likely to result in a conversion.
- AI in the Banking Industry
The banking industry faces serious fraud issues. Like a bank teller who intuitively reads a customer's behavior to spot inconsistencies, zero shot learners can capture a wealth of information during customer interactions and contextualize data to enrich other areas of business operations. The nuanced data, gleaned from multiple customer interactions, can help create a detailed behavioral profile for each customer. Any deviations from “normal” behavior can trigger alerts for potentially fraudulent activity. By providing a more detailed and personalized understanding of customer behavior, generative AI enhances the accuracy of fraud detection and reduces false positives.
How Generative AI Changes the Customer Journey
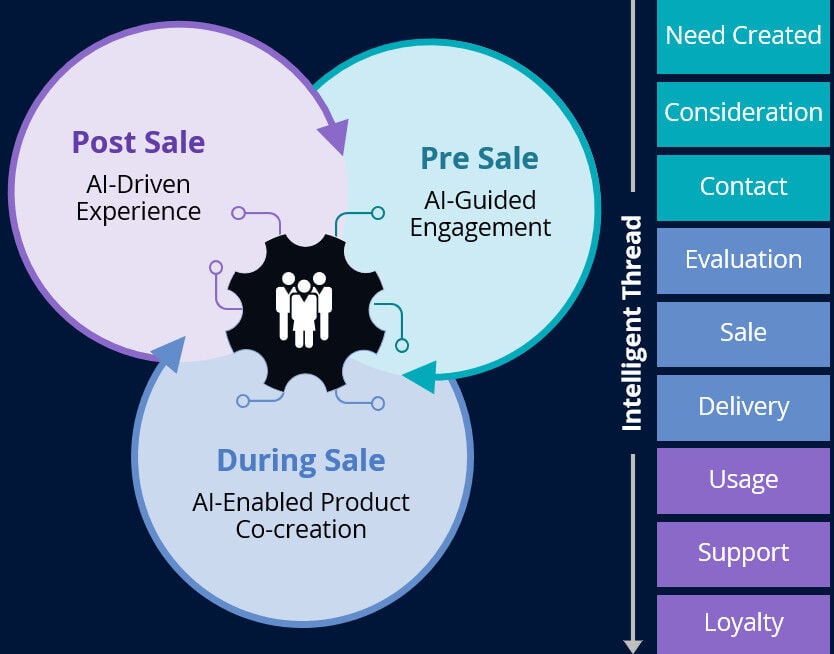
Individual use cases for generative AI demonstrate great potential, but we need to go further and reimagine the entire customer journey. The real power lies in pioneering a new, AI-centric sales process – including both pre-sales and post-sales – and the supporting infrastructure.
AI use cases demonstrate great potential, but now we can go further and reimagine the entire customer journey.
Born-digital companies have caused a sea change for the customer journey. Deep personalization has been achieved across all channels of customer interaction. However, the journey feels “personalized,” not “personal.” While individual steps and interfaces are tuned to a user, the overall arc of the customer journey is fixed. With generative AI tools, it is possible that the journey and the journey steps can be personalized on the fly for different users (and even the same user at different times). The ability to fashion customer interaction pathways dynamically while still maintaining security and transaction integrity is going to be the next inflection point in how companies delight their customers.
By inserting generative AI between pre-sales and post-sales customer interactions, enterprises can improve (pre-sales) product development and recommendation engines and (post-sales) support tools, so they are coordinated and evolve with the needs of the customer. By incorporating these AI tools into business functions that cut across the sales process, companies have the power to offer the deeply personal experience of brick-and-mortar stores while maintaining the efficiencies of digital operations.
Enterprises need to evolve their infrastructure from being designed for human workers to being designed for digital workers. For example, a CRM implementation, which in the past was designed to manipulate and store a lot of complex structured data, will work very differently when AI is involved. Traditionally, organizations spend a great deal of time designing a centralized single-source-of-truth customer record to enable an appropriate interaction with a human agent. But AI can function on far less organized, far less structured data. Unlike a human-centric CRM system, which relies heavily on data warehousing and ETL, AI-powered CRM will not need structured data. Instead, it will need big processing power to work through unstructured data. In essence, the biggest cost for a human-centric CRM implementation is bytes and ETL, whereas for an AI-powered CRM it will be GPUs. Both the infrastructure and the resources will need to shift to make the most of the new capabilities generative AI brings.
Mitigating the Risks of Using Generative AI
Customers are twice as likely to tell someone about a bad service experience than they are to tell someone about a good service experience. The introduction of AI has not changed this. In fact, customer expectations continue to rise. While the promise of AI is great, there is equal danger in going the wrong direction and ending up with a solution that drives customers away.
While the promise of AI is great, there is equal danger in going the wrong direction and ending up with a solution that drives customers away.
For an AI strategy to succeed, enterprises must identify and merge the right set of tools with the right human intelligence. AI technology is advancing quickly, making it a challenge to keep up. This is where a strategic partner network can fill in your knowledge gaps and help you build the best solution for your customers. ISG helps enterprises select, source and implement AI in a strategic way. Contact us to learn more about how ISG can help you find the right partner and bring your AI solutions to life.
