Industry 5.0 is a relatively new concept, originating from Japan's Society 5.0 initiative, and has been adopted by the European Commission's Community of Practice. Despite its growing prominence, Industry 5.0 lacks a clear and unified structure, leading to ongoing debates around its definition.
Unlike Industry 4.0 – which focuses on shopfloor connectivity and automation – Industry 5.0 emphasizes human-centric innovation, with overlap occurring only with specific emerging Industry 4.0 technologies.
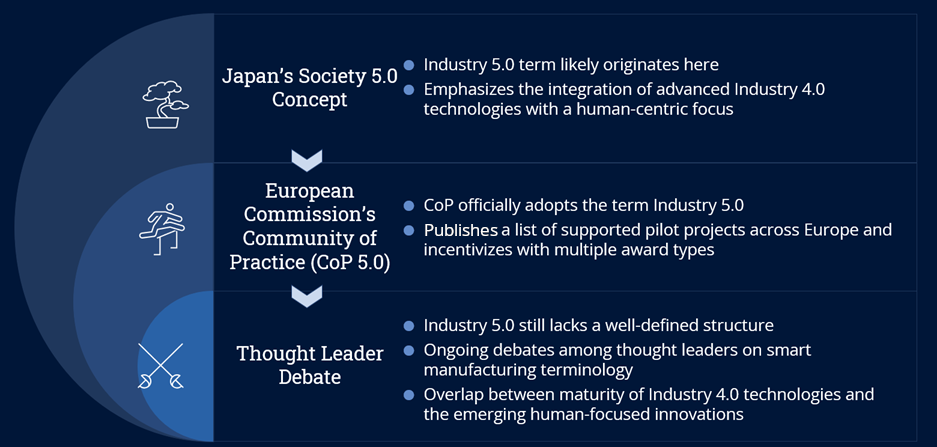
Figure 1: Evolution of Industry 5.0
Human-machine collaboration is the hallmark of Industry 5.0, marking a pivotal shift toward fully automated physical processes.
Industry 5.0 includes the following defining characteristics:
- Human-machine collaboration: Successful tech enhances human capabilities rather than replacing them, using connected tools to boost productivity and quality while eliminating dangerous tasks to reduce injury risk.
- Disruptive AI: Operational leaders are riding the GenAI wave to accelerate product time-to-market by investing in their technology literacy. GenAI is inherently human-centric, translating natural language into structured outputs like code and media content. The next innovation on this level is expected to be private AI, with localized and secure large or small language models hosted on personal devices.
- Sustainability and environmental considerations: Eco-friendly Industry 5.0 practices are guided by environmental consciousness and regulations, with world leaders committing to industry-specific carbon footprint reductions (and eventually net-zero carbon) through waste management and energy efficiency. This approach recognizes the human factor as both an output of industrial manufacturing and as a driving force.
- Customization of craftsmanship: In Industry 5.0, personalized, high-quality production replaces mass production. It is focused on tailored solutions that meet individual needs and preferences, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction and product relevance.
- Quality and precision manufacturing: The use of edge AI in IIoT, enhanced human-machine interfaces, predictive maintenance and other advanced innovations leads to higher-quality products built with better and more accurate processes.
- Supply chain resilience: Manufacturers can now rapidly adapt, recover and maintain operational continuity in the face of global logistics disruptions. This also means risks are mitigated through flexible and sustainable production processes.
- Model infrastructure: Thought leaders are slowly coming together to assess, design and agree on a model infrastructure specific to the new set of technologies. While the characteristics defined in the figure below don’t rigidly define Industry 5.0, they’re identified by their direct impact of Industry 4.0 innovations, which are considered the building blocks of Industry 5.0.
- Based on these industry guidelines, there is a need to adapt and invest in new infrastructure to support the expansion of technologies such as 6G and GenAI.
- Cybersecurity is a key component of this model infra and is considered as one of the required guardrails.
- Dark factories and cobots: Cobots, or collaborative robots, are revolutionizing modern manufacturing by integrating fully automated processes with tasks that still require human skills and judgment. These cobots handle repetitive, mundane tasks, allowing human workers to focus on more complex activities, which leads us into compartmentalized manufacturing such as robotic welding cells – they are also key to decentralized dark factories (DDF), where modular facilities can be deployed with little to no human interaction.
- Scalable local production: Increasing production capacity at the local level usually comes at the expense of quality and cost. However, by adopting highly responsive and adaptive manufacturing, manufacturers can quickly adapt to market demands, reduce supply chain dependencies and maintain reduced carbon footprints.
- Decentralization of intelligence: The decentralization of intelligence shifts decision-making from centralized systems to distributed nodes, allowing human-driven responses that are scalable. For example, edge computing and GenAI allow democratized access to legacy information that was once deemed too expensive to consume.
- Industry 4.0: Technologies focused on connectivity and automation have found success in this industrial revolution and have been tagged as the next generation of long-lasting components of the manufacturing.
- Innovation: Human creativity within industrial automation is focused on creating more efficient and personalized processes, moving beyond simple machine learning into self-empowering innovative spaces.
- 6G: As 5G is slowly being adopted, the availability of this technology is still lacking. It is, however, a cornerstone of connectivity for shop floors and smart cities.
- Safety: All roads lead to Rome. All technology is built with human safety in mind.

Figure 2: Key Characteristics of Industry 5.0
Industrial IoT has played a significant role in Industry 4.0 innovations with moderate success in 5G and edge computing; it highlights the connected nature of this next industrial revolution. Thought leaders have identified three phases of Industry 4.0. Smart manufacturing is in the third wave. Although it is still maturing, this third wave is focused on making advanced tech more available for quantum computing, neurotech and bioinformatics. Notably, these innovations are quite separate from the human-augmenting capabilities of Industry 5.0.
Enterprises should prepare for rapid growth and breakthroughs in the smart manufacturing space. That is what will take them from Industry 4.0 to Industry 5.0.
How Can ISG Help you?
ISG specializes in helping businesses adopt new technologies such as Industrial IoT, GenAI and digital twins. With our expert consulting services, we provide tailored strategies with a robust vendor sourcing approach. We guide enterprises through the complexities of Industry 4.0/5.0 governance, digital transformation and implementing sustainable practices that ensure they stay ahead in the competitive landscape.
