We’re exploring how enterprises should leverage generative AI in a series of articles. In previous articles, we’ve discussed AI’s impact on customer service, product creation and digital threads and twins. In this next article, we are exploring how generative AI can help organizations build adaptive and resilient supply ecosystems.
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, disruptions have become the norm rather than the exception. And the concept of a traditional, linear supply chain is no longer sufficient.
Businesses need to redefine their approach to supply chain management. By building an adaptive and resilient supply ecosystem, companies can position themselves to better navigate disruptions, predict uncertainties and propel innovation.
What Is an Adaptive and Resilient Supply Chain?
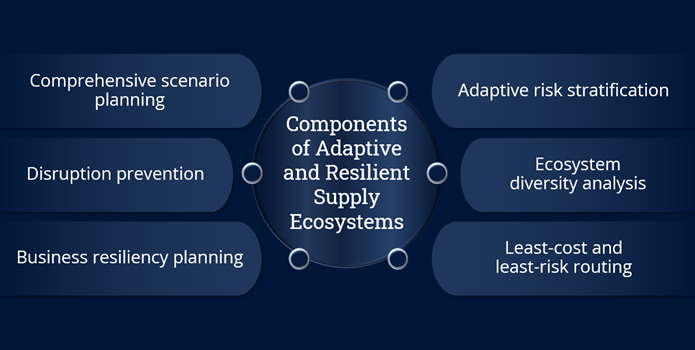
An adaptive and resilient supply chain contains the following six components:
- Adaptive risk stratification: By analyzing historical data, real-time information and AI-driven insights, businesses can allocate resources wisely, pivot strategies quickly and proactively assess risk so their supply chains are protected against uncertainties. Generative AI can be used, for example, to identify and prioritize risks in the retail supply chain, including disruptions to transportation, weather events and product recalls. This information can then be used to develop mitigation strategies, such as building up inventory buffers and working with suppliers to develop contingency plans.
- Ecosystem diversity analysis: By using generative AI to continuously assess supplier, partner and resource diversity, companies can identify and avoid single points of failure. It recommends measures to enhance redundancy, reduce reliance on a single source and create interconnected options for crisis management. When a company uses generative AI is used to create sustainable product designs, for example, it can improve its environmental footprint and customer satisfaction levels.
- Least-cost and least-risk routing: Real-time data and AI-driven insights help companies dynamically route their supply chains to lower risk and be more cost-efficient. Continuous analysis of factors like transportation costs, market dynamics, geopolitical risks and supplier reliability allows companies to reduce expenses and navigate disruptions. For example, a logistics and freight delivery company can use AI to enhance the efficiency of its delivery route planning to reduce fuel consumption and emissions and, at the same time, improve its track record for on-time deliveries.
- Business resiliency planning: Resilient systems are defined by built-in redundancies, flexible capacities and rapid response mechanisms. Generative AI equips supply chains to swiftly adapt, reroute resources and minimize downtime during unexpected disruptions, making business continuity planning an automated, ongoing process. For example, an insurance company can use generative AI to enhance fraud detection capabilities by generating synthetic data to train machine learning models for the detection of fraudulent insurance claims.
- Disruption prevention: Generative AI models analyze diverse factors – from geopolitical events to climate patterns – to be able to predict disruptions. Generative AI's predictive capabilities and data analysis allow enterprises to chart alternate paths, switch suppliers and optimize logistics with flexibility. Generative AI can be used to predict potential disasters, for example, such as power outages or worker strikes, and recommend alternate plans for production.
- Comprehensive scenario planning: Generative AI-driven scenario planning explores a wide range of potential disruptions and responses, giving enterprises a way to design a supply chain strategy that covers numerous variables and reduces the trial-and-error phase during real-world disruptions. When generative AI is used to predict product demand in a network of global stores for a retail company, for example, it helps the company avoid stockouts and overstocks, which can save millions of dollars each year.
Benefits of Generative AI-driven Supply Chains
The following benefits apply to nearly all supply chain use cases for generative AI:
- Improved visibility by providing real-time insights into demand, inventory and transportation, facilitating quicker risk identification and mitigation
- Increased efficiency through task automation and process optimization, freeing up human resources to focus on strategic activities
- Reduced costs through inventory optimization, improved transportation efficiency and waste reduction
- Improved customer satisfaction by providing a more reliable and responsive supply chain that leads to increased sales and loyalty.
Adaptive and resilient supply ecosystems allow organizations to shift away from reactive damage control and toward proactive risk mitigation. These ecosystems are not just about surviving uncertainties; they empower enterprises to thrive, innovate and outpace challenges.
As generative AI continues to develop, it is likely to play an even greater role in the future of supply chain management. This is why a strategic partner network can help define an evolved supply chain, identify risks and develop enhanced solutions for your customers. ISG helps enterprises identify, source and implement AI in a strategic way. Contact us to learn more about how ISG can assist you to identify suitable partnerships and realize your strategic objectives.